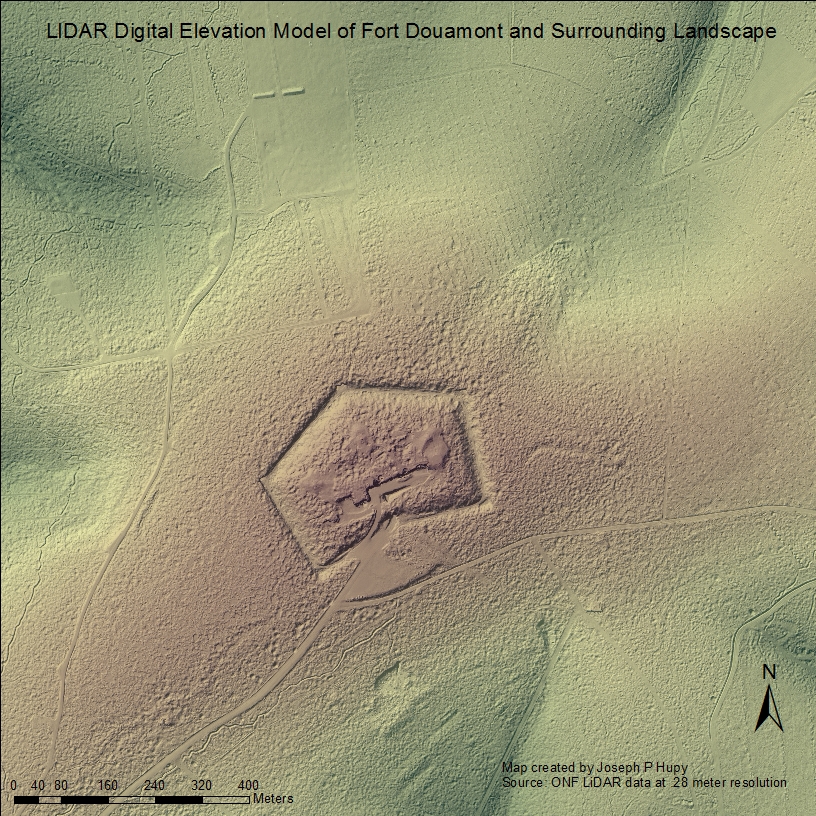
The multiple forms of disturbances rendered by conflict upon landscapes around the world demonstrate that this anthropogenic agent is an incredible force that is capable of exerting an influence on the environment in a wide variety of ways, yet the bridge between geomorphology and environmental histories of battlefields is rarely made. This research associated with this presentation examines two case study battlefields, and how post-conflict land-use patterns are tied into what we see on the contemporary landscape of today. Also emphasized in the presentation are how various geospatial data collection tools and methods can be utilized with geospatial software to model the changes rendered to landscapes due to conflict, and to link these disturbances with modern land-use patterns.
Joe Hupy (Associate Professor of Geography, University of Wisconsin – Eau Claire)
Joseph Hupy earned his PhD in geography from Michigan State University using soils as a proxy indicator for landscape stability following disturbances rendered by explosive munitions in World War One. Out of that research he coined the term ‘bombturbation’, which describes how soils are disturbed from explosive munitions, one of many forms of anthropogeomorphology where humans shape the landscape. The research surrounding World War One bombturbation led towards examination of other battlefields around the world, including research forays on the Viet Nam battlefield of Khe Sanh in 2007 and 2009. Research on all these battlefields relied upon a myriad of geospatial equipment and Geographic Information System modeling techniques. Out of that research and most recently, Joe has begun to use Unmanned Aerial Systems as a tool to gather data, and hopes to revisit other world battlefields in collaboration with other researchers in different disciplines using this technology as a tool.